Technology Overview & Trends
A global leader of the world display market — STEMCO

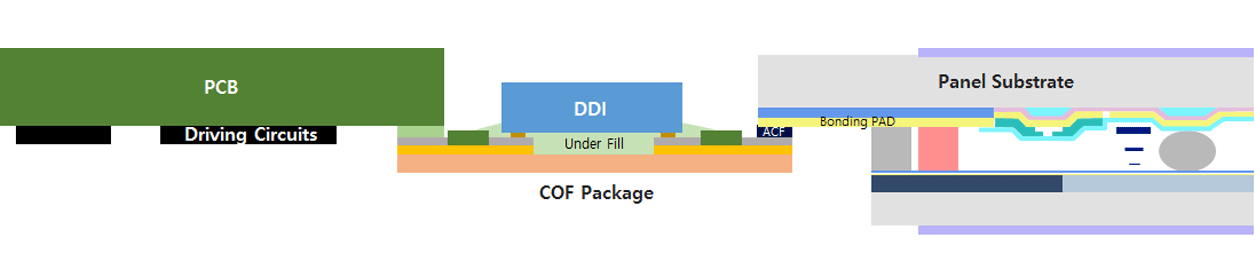
Introduction to the TCP
TCP (TAPE CARRIER PACKAGE)
- TCPs use a tape film as a mounted board on which TAB (Tape Automated Bonding) TAB films and Flip Chip Bonding (or LOC) COF films are combined.
- A TAB film consists of 3 layers: the board of a polyimide film, adhesive layer, and the copper foil.
The copper foil consists of the inner lead connecting the Display Driver IC in a way of die bonding through Au Bump and the outer lead mounted on a glass board or PCB.
Basically, a COF film has the same function with a TAB film, but it uses the double-layered raw materials — Cu-coated polyimide films — to secure high flexibility and fine pitch performance.
TCP History
The TAB is a package introduced in the late 1980s for lead embedding of multiple semiconductors. It entered the growth period around 1988 when starting to be used for Display Driver ICs.
The COF was developed in the late 1990s as a placement of the TAB in response to fine pitch formation in driver ICs as large-size/high-resolution displays were developed.
Now the COF is commonly used.
TCP (COF) Functions
The display module consists of the panel, driver IC, and PCB circuit components.
The TCP (COF) represents screen colors by connecting electric signals mutually.